What is labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty is the reduction of the labia minora (inner lips around vagina) or labia majora (outer lips), performed for cosmetic and/or medical reasons.
Who is a candidate?
Labiaplasty has become a more popular procedure, due in part to greater awareness that the surgery even exists, more acceptance talking about preferences in the genital region, and grooming trends towards hairless or minimal hair styles. It’s important to know that “normal” labia come in different shapes, sizes, colors, and textures. While many women prefer a neat, trim look, there also are those who prefer a natural look, no matter how large their labia or what their color. Ultimately, it’s a personal decision whether or not you want to undergo the procedure.
Common reasons for having labiaplasty include:
- Preference for a neat, trim appearance
- Correcting asymmetry
- Pain with sexual intercourse
- Decreased clitoral stimulation when excess skin covers the area
- Difficulty with hygiene
- Pain or discomfort with activities such as bike riding
- Difficulty wearing certain clothing, such as fitted pants or exercise wear
- Friction or pulling with exercise
Is it okay for a woman over 50 to have a labiaplasty?
Yes, it is okay. The area loses volume with age, and this can make the skin seem droopy or deflated. Options for improvement of excess or droopy skin include labiaplasty as described above, and options for volume loss include fat transfer or fillers to the outer labia.
Labiaplasty Techniques
There are many different techniques for labiaplasty. The three most common are the trim (or amputation), the wedge, and the modified or extended wedge.
With the trim technique the labia minora (the inner lips around the vagina) is clamped and amputated, and each of the two sides is sewn up with a running baseball-style stitch. The procedure takes about 1 hour. The potential disadvantages are 1) having too much of the labia removed, which causes the vagina and urethal opening to lose protection, as well as cosmetic disfigurement, 2) having a more obvious scar on the border of the labia, and 3) reportedly greater risk of pain along the scar.
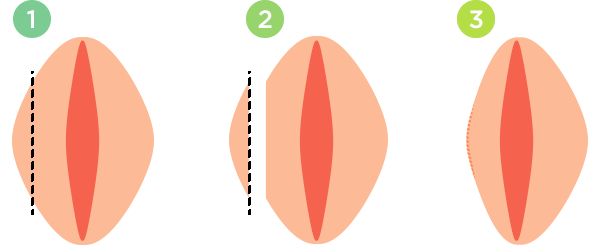
Diagram of the trim technique.
The wedge technique takes a wedge, or V-shaped excision, from the center of the excess labia. Considered better than the trim technique, this procedure preserves the natural transition at the border of the labia. The procedure takes 1 to 1.5 hours.
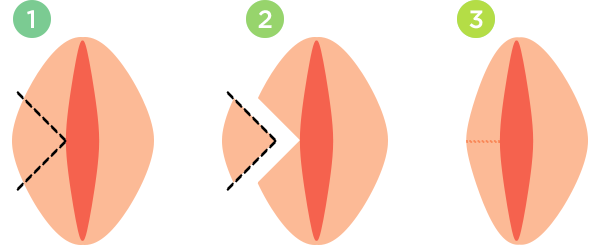
Diagram of the wedge technique.
The modified or extended wedge technique takes a wedge from the inner labia skin, as well as a downward facing wedge from the outer labia. Scars are difficult to detect after healing. Dr. Patel prefers the extended wedge procedure, which takes about 1.5 to 2 hours.
Clitoral Hood Reduction
Clitoral hood reduction can be done at the same time as labiaplasty, or as a stand alone procedure. The entire area needs to be evaluated as a unit, and the relationship and proportions need to be adjusted if necessary. Some patients have extra skin at the clitoral hood and the labia, and if only the labia are addressed, the upper half of the region looks abnormal. Dr. Patel does a conservative excision of tissue in this area due the sensitive nature of the anatomy. This procedure adds about 20 to 30 minutes to a labiaplasty surgery.
Can I be awake for labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty can safely be performed under local or general anesthesia. Labiaplasty with general anesthesia is typically preferred for patient comfort throughout the process.
What are the risks of labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty is a safe procedure when performed by appropriately trained surgeons in an accredited facility. The doctor will discuss standard risks, ranging from pain, bleeding and infection to scarring; swelling and changes in feeling.
Recovery after Labiaplasty
Recovery from surgery takes around one week, when you can return to work and normal activities. However, sexual intercourse and strenuous activity is not advised for the first 8 weeks following surgery.


